Physical Characteristics
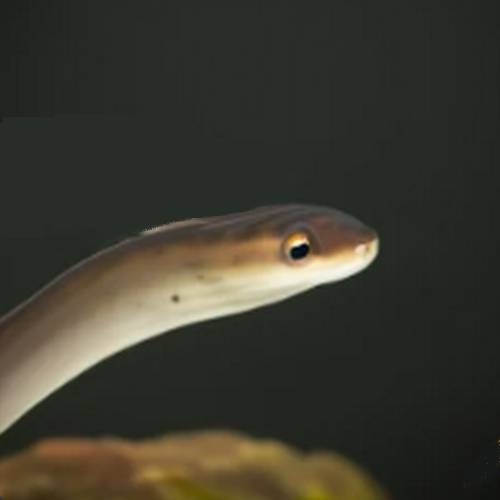
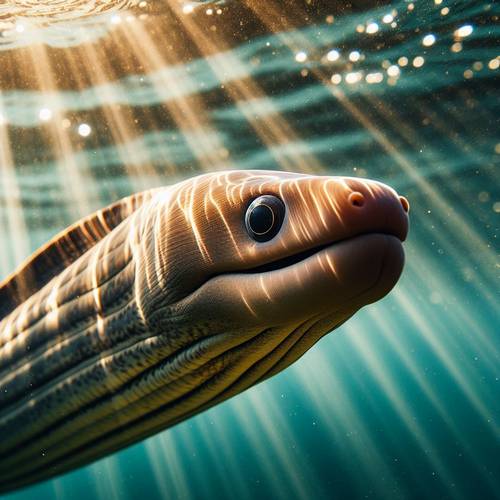
Boasts unique physical characteristics, the American Eel growing up to 4 feet long, its slender, snake-like body is covered in a mucus layer that gives it a distinct silver appearance. This elusive species possesses a remarkable ability to adapt to various environments, thriving in both freshwater and saltwater habitats.
With a lifespan of up to 20 years, these American Eels are known for their incredible migratory journeys, spanning thousands of miles. Understanding these essential traits is crucial for conserving this American Eel species, as they play a vital role in maintaining the balance of aquatic ecosystems.
With a lifespan of up to 20 years, these American Eels are known for their incredible migratory journeys, spanning thousands of miles. Understanding these essential traits is crucial for conserving this American Eel species, as they play a vital role in maintaining the balance of aquatic ecosystems.
Historical Significance
This species holds immense historical significance, dating back thousands of years. Native American tribes revered it as a symbol of resilience and adaptability. Its cultural importance is evident in art, folklore, and ceremonies. Scientifically, the species has intrigued researchers for its extraordinary migratory behavior, with individuals traveling over 2,000 miles during their lifetime.
Unfortunately, recent studies indicate a decline in its population, making conservation efforts crucial. Preserving the American Eel not only safeguards biodiversity but also honors the legacy it has held for generations.
Unfortunately, recent studies indicate a decline in its population, making conservation efforts crucial. Preserving the American Eel not only safeguards biodiversity but also honors the legacy it has held for generations.
Economic Importance
Eel holds significant economic importance in various ways. Fisheries and commercial industries heavily rely on this species for trade, contributing an estimated $40 million annually to the economy. Additionally, the eel serves as a vital component in recreational fishing, drawing thousands of anglers each year, boosting tourism and local businesses.
However, overfishing and habitat degradation pose threats to its population, necessitating conservation efforts to maintain its economic value and ecological role. Protecting this unique creature is crucial for sustainable economic growth and the health of aquatic ecosystems.
However, overfishing and habitat degradation pose threats to its population, necessitating conservation efforts to maintain its economic value and ecological role. Protecting this unique creature is crucial for sustainable economic growth and the health of aquatic ecosystems.