Description
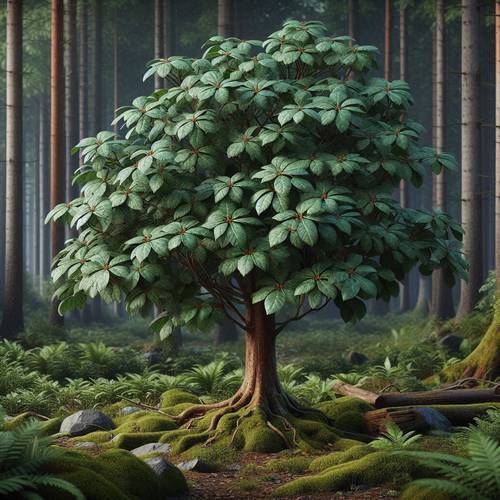
The Sassafras albidum, commonly known as the Sassafras tree, is a captivating sight in the American landscape. This deciduous tree, a member of the Lauraceae family, is renowned for its distinctive leaves, fragrant bark, and flavorful roots.
Sassafras trees are known for their unique leaf shapes. They can have leaves that are oval, two-lobed, or three-lobed, with the three-lobed leaves resembling a mitten or a paw print. The leaves are green in the summer, turning vibrant shades of yellow, orange, and red in autumn, making them a beautiful addition to any landscape.
The bark of the Sassafras tree is rough and deeply furrowed, with a distinctive cinnamon-brown color. The tree also produces small, yellow flowers in the spring, followed by dark blue berries that are clustered together.
Sassafras trees are known for their unique leaf shapes. They can have leaves that are oval, two-lobed, or three-lobed, with the three-lobed leaves resembling a mitten or a paw print. The leaves are green in the summer, turning vibrant shades of yellow, orange, and red in autumn, making them a beautiful addition to any landscape.
The bark of the Sassafras tree is rough and deeply furrowed, with a distinctive cinnamon-brown color. The tree also produces small, yellow flowers in the spring, followed by dark blue berries that are clustered together.
Distribution and Habitat
This tree is native to the eastern United States and southeastern Canada. Its natural range stretches from Maine and southern Ontario in the north, southward to Florida and Texas. Sassafras trees are typically found in moist, well-drained soils, thriving in a variety of habitats, including forests, woodlands, stream banks, and fields.
They are adaptable trees, preferring full sun to partial shade and can tolerate a wide range of soil conditions. They are often found in mixed forests, alongside other deciduous trees such as oak, hickory, and maple. Sassafras trees are a common sight in the Appalachian Mountains and the Ozark Mountains, where they are often found growing near streams and rivers.
They are adaptable trees, preferring full sun to partial shade and can tolerate a wide range of soil conditions. They are often found in mixed forests, alongside other deciduous trees such as oak, hickory, and maple. Sassafras trees are a common sight in the Appalachian Mountains and the Ozark Mountains, where they are often found growing near streams and rivers.
Identification
Identifying Sassafras trees is relatively straightforward thanks to its unique characteristics.
Here are a few key features to look for:
• Three-lobed leaves: Sassafras trees are the only trees in North America with three-lobed leaves, making this a distinguishing feature. These leaves have a mitten-like or paw-print shape.
• Aromatic bark: The bark of the Sassafras tree has a distinctive, spicy scent, particularly noticeable when scratched or broken.
• Root system: While not easily visible, the roots of the Sassafras tree are thick and woody and have a strong, sweet, root beer-like aroma.
• Small, yellow flowers: Sassafras trees produce small, yellow flowers that grow in clusters during the spring. These flowers are followed by dark blue berries that are clustered together.
**By observing these unique characteristics, you can easily identify the Sassafras albidum tree in its natural habitat.
Here are a few key features to look for:
• Three-lobed leaves: Sassafras trees are the only trees in North America with three-lobed leaves, making this a distinguishing feature. These leaves have a mitten-like or paw-print shape.
• Aromatic bark: The bark of the Sassafras tree has a distinctive, spicy scent, particularly noticeable when scratched or broken.
• Root system: While not easily visible, the roots of the Sassafras tree are thick and woody and have a strong, sweet, root beer-like aroma.
• Small, yellow flowers: Sassafras trees produce small, yellow flowers that grow in clusters during the spring. These flowers are followed by dark blue berries that are clustered together.
**By observing these unique characteristics, you can easily identify the Sassafras albidum tree in its natural habitat.