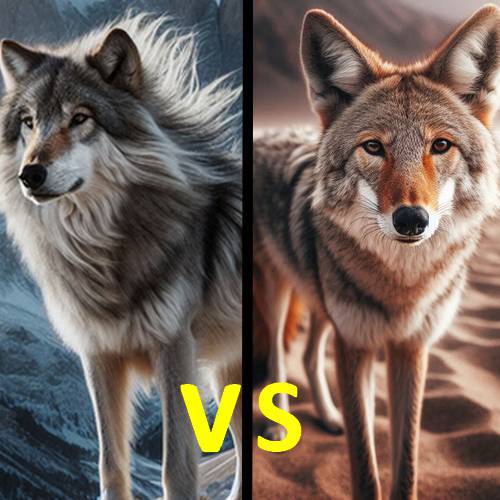
Wolves and coyotes are both canids, but they exhibit distinct physical differences.
• Wolves are significantly larger, with males averaging 100-175 pounds and females 70-130 pounds.
• Coyotes are much smaller, typically weighing 25-50 pounds. This size difference is evident in their overall build, with wolves having a more robust and muscular frame.
Appearance-wise, wolves have a more massive head with a wider muzzle, while coyotes have a more slender, fox-like head. Wolves typically have a stockier build with shorter legs compared to the longer legs and more slender build of coyotes.
Their fur colors also differ, with wolves sporting shades of gray, black, and brown, while coyotes range from a grayish-yellow to a reddish-brown. These physical distinctions help distinguish these fascinating canids in the wild.
• Wolves are significantly larger, with males averaging 100-175 pounds and females 70-130 pounds.
• Coyotes are much smaller, typically weighing 25-50 pounds. This size difference is evident in their overall build, with wolves having a more robust and muscular frame.
Appearance-wise, wolves have a more massive head with a wider muzzle, while coyotes have a more slender, fox-like head. Wolves typically have a stockier build with shorter legs compared to the longer legs and more slender build of coyotes.
Their fur colors also differ, with wolves sporting shades of gray, black, and brown, while coyotes range from a grayish-yellow to a reddish-brown. These physical distinctions help distinguish these fascinating canids in the wild.